Home»Garden»Compost & Soil Health
Last Updated on August 9 , 2023
Have you heard about craw gyration , but are n’t trusted what it ’s all about ? Or , wondering if it ’s something you should be doing ? Then you ’ve come to the good berth . This article will give you the flying - and - dirty on crop rotation : what it is , the benefits it can provide to plant and the surround , and how to practice it in your garden . I ’ll play up and ply examples of using the 4 - class cycle per second or “ 4 harvest rotation ” method specifically . To be honest , we are n’t perfect in harvest rotary motion efforts in our garden – but it ’s something we do test to be mindful of !

What is Crop Rotation?
Crop rotation is the pattern of interchange or switching the crops that are mature in a particular location ( for example a field , plot or garden bed ) every time of year . In other Scripture , it ’s when a husbandman or gardener makes a concerted endeavour to avoid growing the same family unit of vegetables in the same stain year after year . It is an essential component in regenerative andsustainableagriculture organisation , alongside goodmulch , garden companion planting , andno - till or no - digpractices .
Crop revolution can be as simple as change over between two different harvest families , or developing a contrive sequence of up to a 12 crops . Allowing discipline to fallow ( go unplanted ) or utilizing cover crops between season can also be part of a crop rotation routine .
Would you like to save this?
We ’ll email this post to you , so you may arrive back to it later !
I agree to receive email updates .
revealing : Homestead and Chill is proofreader - bear . When you purchase through link on our website , we may earn an affiliate commission .

Why Crop Rotation is Important
There are numerous welfare to crop rotation . First , practicing craw rotation can naturallyenhance soil fertilityand reduce the demand for chemic fertilizer stimulation . Even better , researchindicates that crop production can be 10 to 25 % greater when crop revolution is used in comparison to monoculture polish !
Crop revolution can also aid break the Hz ofpests , disease , and weed , thereby decreasing the motive for pesticide . The use of cover crop in crop rotation improves soil health while also minimize soil corrosion and runoff .
The Rodale Instituteexplains that harvest rotation can ameliorate grime health and organic matter “ by increasing biomass from dissimilar crops ’ root structures ” while increase overallbiodiversityamong the grime and farm . Below ground , microorganisms and other members of the filth food web naturally fly high with kind – as do the beneficial worm , pollinator , and wildlife above ground !

Now let ’s take a deeper smell at a duet of these welfare .
How crop rotation improves soil fertility
Each character of flora draw slightly different nutrients from the soil . For example , tomatoes , leafy greens and Zea mays require a honest amount ofnitrogen . On the other hand , legume such as pea and beans fix N from the atmosphere and retrovert nitrogen to the soil as they grow ! Continuously planting the same crop ( or members of the same plant life home ) in one localization will easily lead to nutrient depletion or imbalance . In contrast , craw rotation allows the grunge to rest , resile , and retrieve Libra the Balance between seasons .
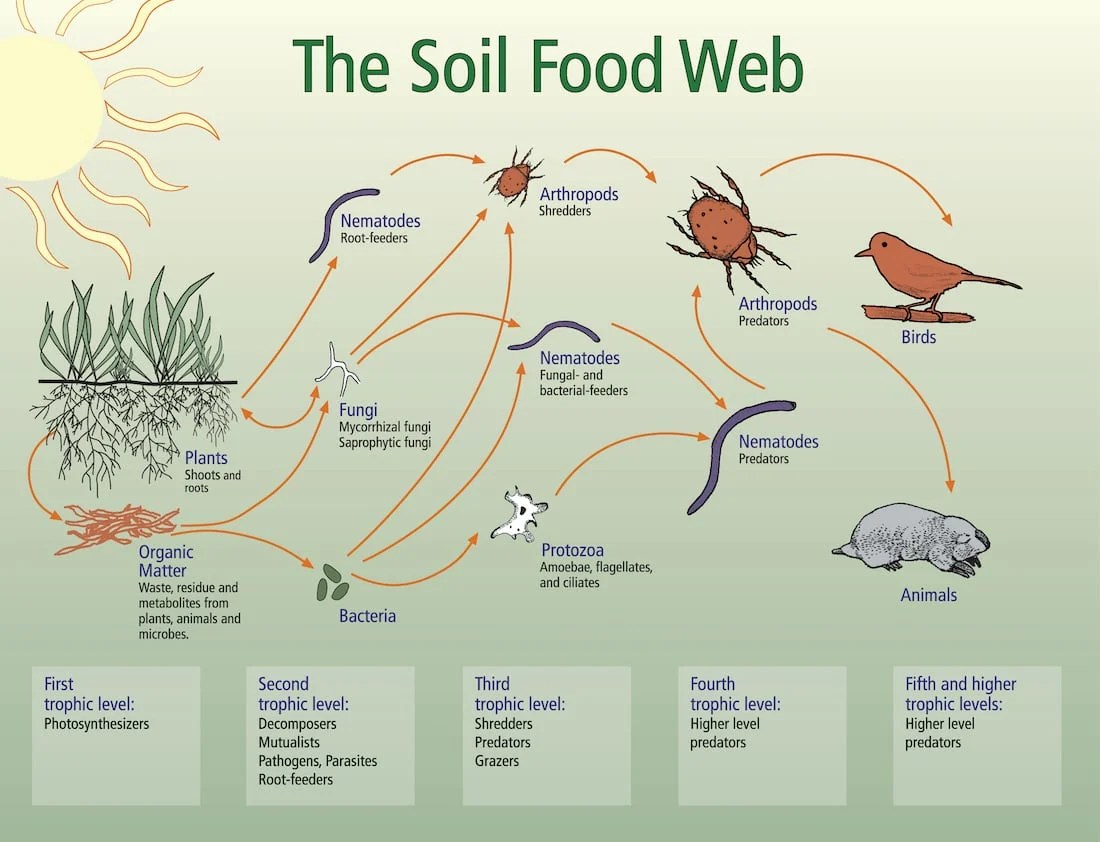
This conception extends beyond macronutrients like atomic number 7 , phosphorus , and potassium ( NPK ) tomicronutrients , minerals , and even microorganisms as well . The ‘ soil food web ’ is a active community of bacterium , fungus , protozoa , nematodes and other critters that dwell in the dirt . They ’re all intimately involved in nourishing cycling , chemical decomposition reaction , disease inhibition , and overall grease wellness .
The more diverse planting we bring home the bacon ( include through crop rotation ) , the more the soil food web thrives – as do our plants !
How rotating crops reduces pests and disease
Crop rotary motion can break the cps of disease or pests byremoving the preferred host plantfrom the sphere . Once establish during the grow time of year , disease - causing fungal spore or soil - dwell organisms like cutworms , root - knot nematodes , orcurl grubscan overwinter in the territory – ready and wait to pounce on their favorite victim the following time of year ! Growing a different or less susceptible harvest in that location instead can abridge or reject the plague / diseases power to procreate or survive .
Considerpowdery mildewfor example ( aka PM , a common fungal disease in our garden ) . If ourzucchiniplants were importantly infect with powdery mold during the grow season , I ’d seek to plant something less susceptible to mold in that placement next . ( Such as radish , Piper nigrum , fava bean , onions , cultivated cabbage , or Brassica oleracea botrytis . ) It ’d be wise to to deflect growing other PM - prone crop like Lycopersicon esculentum , noodle , or more squash in that smirch for a time of year or two . They would only encourage the fungal spore to proliferate .
Is crop rotation necessary in raised beds or home gardens?
Yes and no . Maybe so ? Practicing craw rotation is an splendid goal in any scope , including kindle garden bed or small-scale plot ! Home gardeners can reap many of the same benefit as turgid farm . Rotating crops in raised bed can be specially utilitarian for cut the prevalence of persistent diseases and plague .
However , us house gardener already grow far more variety in our garden than most larger operations . Many of us practicepolyculture , or planting a mix of several types of crop in one minuscule growing outer space or bed . I do n’t know many nurseryman that grow justonething in the same bed year after class … do you ? That said , crop rotation propose thelargest impactand environmental benefits when used as an counterpoison or alternative to large - plate monoculture ( the finish of a single harvest ) – which is commonly practice in big ag , not at home .
what is more , it is admittedly more difficult for a home gardener to practice “ perfect ” crop rotation , specially with circumscribed growing space ! We often ca n’t afford to give up an entire bottom to fallow or grow cover crops every season . If you have several raised garden beds , it ’s idealistic if you’re able to rotate crop amongst different bed each season . However , even the wide-eyed human activity of planting crops in alternating ending or side of one bed is better than nothing !

Just remember : perfection is not the destination . taste your best with the outer space you have . And do n’t leave to addcompanion plantsto promote your harvest revolution efforts !
How to Practice Crop Rotation
In the most basic crop gyration drill , plainly seek to rise different plant families in your bed or rows every other season . More complex rotations may span several twelvemonth and affect importantly more crop , planning , and strategy . vulgar crop revolution schedule for large farms admit cycle between corn , wheat , legume , and other crops .
Small farm and serious home base gardeners can consider practice afour - yr crop gyration cycles/second , switch between :
select any of the highlighted veg above to see our correspondinggrow guide !

In a four - year crop rotation , when you lead off the cycle does n’t count , but theorderdoes .
Thelegumesfix nitrogen from the atmosphere , adding to the ground . Thegreens and brassicasthat observe then utilize a lot of nitrogen to support their leafy increase . By using up some nitrogen , the greens are also preparing the ground for the next group . Next , fruiting vegetablesneed sizable Lucifer to develop flush and fruit ( and will focalise too much on leafy green outgrowth rather of fruit if they ’re leave too much nitrogen ) . eventually , theroot veggiesare the least arduous feeder , but perform best with more potassium and phosphorus than nitrogen . Then the cps starts all over again with nitrogen - repair legumes .
How to Keep Track of Crop Rotation
The most difficult part of do craw revolution can be go along track ! apply aplanner , spreadsheet or chartto keep cut of what you ’re arise in each bed every time of year . Then you’re able to front back at previous years and also plan ahead for the future . We like to utilise ourHomestead and Chill patch plansto map out our garden each planting time of year . In addition to serving as a great computer address for years to come , they facilitate me plan how many seeds to start and maketransplanting daymuch more tranquil and organized !
Some organize nurseryman ( and serious crop rotators ) move their crops from bed to bedin sequencewith the four - yr crop rotary motion cycle . See the model below . We’ve never had enough elbow room to keep up a model quite like this in the past . But now that we have more raised bed in our young garden , we may give it a try ! However there are other variable we postulate to consider too , such as which seam receive the best Lord’s Day for the heat - sleep together crop versus others where more nuance - large-minded plants may thrive .
Do I still need to fertilize if I practice crop rotation?
While it ’s outstanding for the grime , you may not be able to rely on crop rotation alone to adequately nourish your plant . We recommend amending garden beds with agedcompostand a top - dressing of meek , slow - release , well - balancedorganic fertilizereach season . Throughout the growing season , we also like to water our garden beds withaerated compost tea – which provides easy food and boosts good microorganism . you’re able to get our full garden bottom amendment routinehere .
And that’s the 411 on crop rotation.
Do n’t lack these awesome articles :








